Page 14 - E-BOOK English
P. 14
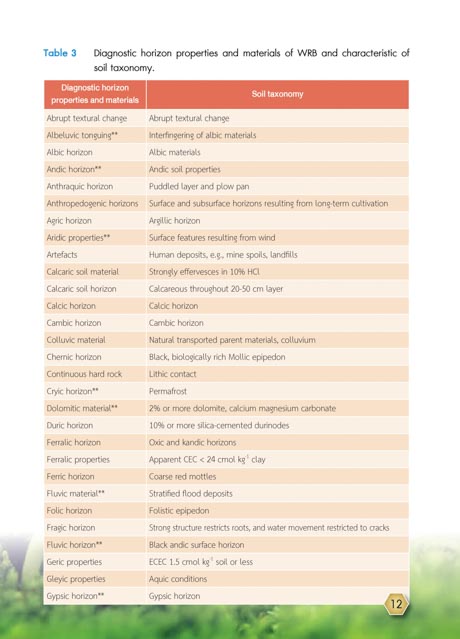
Table 3 Diagnostic horizon properties and materials of WRB and characteristic of
soil taxonomy.
Diagnostic horizon
properties and materials Soil taxonomy
Abrupt textural change Abrupt textural change
Albeluvic tonguing** Interfingering of albic materials
Albic horizon Albic materials
Andic horizon** Andic soil properties
Anthraquic horizon Puddled layer and plow pan
Anthropedogenic horizons Surface and subsurface horizons resulting from long-term cultivation
Agric horizon Argillic horizon
Aridic properties** Surface features resulting from wind
Artefacts Human deposits, e.g., mine spoils, landfills
Calcaric soil material Strongly effervesces in 10% HCl
Calcaric soil horizon Calcareous throughout 20-50 cm layer
Calcic horizon Calcic horizon
Cambic horizon Cambic horizon
Colluvic material Natural transported parent materials, colluvium
Chernic horizon Black, biologically rich Mollic epipedon
Continuous hard rock Lithic contact
Cryic horizon** Permafrost
Dolomitic material** 2% or more dolomite, calcium magnesium carbonate
Duric horizon 10% or more silica-cemented durinodes
Ferralic horizon Oxic and kandic horizons
Ferralic properties Apparent CEC < 24 cmol kg clay
-1
Ferric horizon Coarse red mottles
Fluvic material** Stratified flood deposits
Folic horizon Folistic epipedon
Fragic horizon Strong structure restricts roots, and water movement restricted to cracks
Fluvic horizon** Black andic surface horizon
-1
Geric properties ECEC 1.5 cmol kg soil or less
Gleyic properties Aquic conditions
Gypsic horizon** Gypsic horizon
12